Figueres-Perpinyà high-speed line (2015)
Contract with TP-Ferro and the BRGM to issue urgent and automatic communications in the event of an earthquake that could disturb the operation of the trains that run along the high-speed line on the Figueres-Perpinyà section, according to the protocols defined with TP-Ferro.
Institut Cartogràfic i Geològic de Catalunya (ICGC); TP-Ferro, Spain-France; Bureau de Recherches Géologiques et Minières (BRGM), France.
Wi-GIM Remote sensor network for the monitoring of ground instability (2014-2017)
The project aims to develop, implement and test an innovative wireless sensor network (WSN) for 3D surface tracking of terrain deformations, such as landslides and subsidence. Its purpose is to build and demonstrate the feasibility of a low-cost system (Wi-GIM system) that allows remote and accurate deformation monitoring. It is based on two types of wireless device: the sensor nodes (SN) and the base stations (BS). The movement of the surface is detected by acquiring the position (x, z) of each SN organized in a WS. The position is determined by the innovative integration of the LB technology, capable of detecting the 3D coordinates of the sensor with a submetric error, with the continuous-wave radar (CWR), which allows to reduce the error below cm.
Institut Cartogràfic i Geològic de Catalunya (ICGC) and other participating organizations: International Consortium on Advanced Design (ICAD); Dipartamento di Scienze della Terra (Università degli Studi di Firenze), Italy; Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia (INGV), Italy; Regione Emilia Romagna (RER), Italy.
Co-financed by: LIFE + Program (EU).
ALERTES-RIM. Earthquake Early Warning: Regional and in situ System for the ibero-maghrebian region (2014-2016)
Earthquake Early Warning Systems (EEWS) are one of the most effective and innovative tools developed in the last decade and the one that has created more expectation among the institutions involved in the study and the management of seismic hazard. The aim of one EEWS is to prevent and minimize the damage caused by earthquakes.
The purpose of the ALERTES-RIM project is to develop an EEWS for the ibero-maghrebian region that includes earthquakes that affect Portugal, Spain, Morocco and Algeria, and to benefit from the results obtained in a previous project (ALERT-ES) in which took part the same institutions.
The most relevant aspects of the ALERTES-RIM project are: the inclusion of the entire ibero-maghrebian region in the EEWS, the use of various parameters corrected by the site effect to obtain empirical laws of magnitude, the determination of an equation of prediction of soil movement for the whole region, the generation of theoretical seismograms to supply the lack of digital records of large earthquakes, the joint development of a regional and in situ EEWS for the area, the optimization of reaction times and the evaluation of the incorporation of GPS data in the EEWS.
Universidad Complutense de Madrid (UCM), Spain; Real Instituto y Observatorio de la Armada (ROA), Cádiz, Spain; Institut Cartogràfic i Geològic de Catalunya (ICGC).
Financed by: Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad.
DinSAR in the city of Bogotá (2014)
The ICGC studied, with differential interferometry techniques with synthetic aperture radar (DinSAR), the evolution of ground subsidences in the city of Bogotá during the 2011-2012 period, based on satellite images.
Institut Cartogràfic i Geològic de Catalunya (ICGC) and other participating organizations: Fondo de Prevención y Atención de Emergencias de Bogotá, D.C. (FOPAE), Bogotá, Colombia.
Financed by: Fondo de Prevención y Atención de Emergencias de Bogotá, D.C. (FOPAE), Bogotá, Colombia.
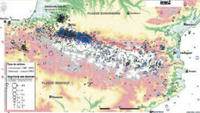
iCoast. Integrated Coastal Alert System (2013-2015)
The main objective is to develop a tool (iCoast: Integrated Coastal Alert System) to manage coastal risks caused by extreme waves and high sea water levels in European coastal areas. ICoast will be used as an Early Warning System to forecast storm events and help managers in the decision-making processes. The main targets will be urban beaches and coastal defences and infrastructures where most of the casualties are reported. The two-year project will deliver a prototype of a coastal early warning system which will include the protocols of interventions and alert information and a map of the most relevant coastal hazards and associated risks over the Western Mediterranean coast. This will allow defining a series of guidelines and best practices and the lessons learnt of interventions.
Institut Cartogràfic i Geològic de Catalunya (ICGC) and other participating organizations: International Center of Coastal Resources Research; Soluciones de Ingeniería Marítima Operacional (SIMO), Spain; Servei Meteorològic de Catalunya (SMC); Centre d’Emergències de Catalunya (CECAT, INT ES); Information Technology for Humanitarian Assistance, Cooperation and Action (ITHACA), Italy; University College Cork (Coastal and Marine Research Centre, CMRC), Ireland.
Financed by: Civil Protection instrument (EU).
GAL. Galileo for gravity (2012-2014)
The aim of this project is to study and to establish the state of the art on the methodology for the determination of the gravimetric field in a precise way and in high resolution by means of the Kinematic Airborne Gravimetry (KAG) from the data of the global positioning system (GPS), the European geostationary navigation system (EGNOS), the future GALILEO positioning system and "strapdown inertial measurement units" (IMU), and its subsequent integration with global gravimetric models derived from the European satellite GOCE .
Galileian Plus, s.r.l., Italy; Politecnico di Milano, Italy; Consorci Institut de Geomàtica, Spain; DEIMOS Engenharia, SA, Portugal; Institut Geològic de Catalunya (IGC); École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, Switzerland.
Financed by: 7th Framework Programme.
ALERT-ES. Early warning system: implementation in southern Spain C-3 (2011-2013)
The main goal is to study the feasibility of an Earthquake Early Warning System (EEWS) for the potentially damaging earthquakes that occur in the region of Cape S. Vicente – Gulf of Cádiz, based on the real-time applications existing in the IGC.
Institut Geològic de Catalunya (IGC); Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain; Real Instituto y Observatorio de la Armada (ROA), Spain.
Financed by: Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación, Spain.
FASE. Fractures: Seismic and electrical anisotropy (2011-2012)
The goal of the project is to develop and to test methods of measurement and joint inversion of geoelectrical and seismic data, to study aspects of anisotropy and water flows in areas of mining interest. The study areas are a low noise underground laboratory (Laboratoire Souterrain à Bas Bruit - LSBB), near Rustrel (Marseille), and a AREVA site in Lodève (Montpellier). It is planned to do a monitoring to test, in a 2D and / or 3D configuration, the working hypotheses related to the variation of the seismic and electrical anisotropy according to the type of filling of the fractures. Seismic and electrical joint investment software will be developed and 3D anisotropic models will be built in the laboratory to test the anisotropic properties in a controlled environment.
Université Paris Sud, France; Université Nice, France; Université de Pau, France; Institut für Geophysik (Universität Münster), Germany; UB-Geomodels, Spain; Institut Geològic de Catalunya (IGC).
Financed by: Institut National des Sciences de l'Univers (INSU) of the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS), France.
Classification of the soils in which the new LIS accelerographic stations are located, using methods based on environmental vibrations, Costa Rica (2011-2012)
The goal of the project is the classification of the new accelerographic stations in Costa Rica, applying passive seismic survey techniques. We will study 10 sites with already installed stations and 10 rocky sites for the installation of new equipment. The main purpose is to take advantage of the experience, both in field work and in data processing, which have been acquired by the Seismic Engineering Laboratory of Costa Rica (Laboratorio de Ingeniería Sísmica - LIS) and the IGC.
Laboratorio de Ingeniería Sísmica (LIS) of the Universidad de Costa Rica (UCR); Institut Geològic de Catalunya (IGC).
Financing: Comisión de Incentivos del Ministerio de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONICIT), Costa Rica; Ministerio de Ciencia y Tecnología (MICIT), Costa Rica.
Exchange experiences Delft (2010-2013)
Information exchange and collaboration with the Delft University of Technology (TU Delft) in aspects of cartography, geotechnics (sampling and laboratory techniques), geophysics, geological hazards, water resources, remote sensing and satellite imagery. The IGC collaborates in the fieldwork that TU Delft carries out in Catalonia.
Technische Universiteit Delft, The Netherlands; Institut Geològic de Catalunya (IGC).
Financed by: Participating institutions.
PIERCO2. Advances in electromagnetic research of geological CO2 reservoirs (2010-2013)
Development of a methodology to apply electromagnetic methods and passive seismic surveying for the characterization of suitable sites to store CO2, to monitor and to model them. The validation of the methodology is carried out in a pilot area of the Basque Basin (Hontomín, Burgos), proposed by CIUDEN, and is applied in an area of the intermediate basin proposed by the IGME.
Universitat de Barcelona (UB); Institut Geològic de Catalunya (IGC); Instituto Geológico y Minero de España (IGME), Spain.
Financed by: Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación, Spain.
Transfer of experiences in seismic microzoning in urban areas. Salta, Argentina (2010)
Exchange of experiences on research related to soil response to seismic vibrations caused by moderate and intense earthquakes, presented by each working group of both institutions. With this knowledge, and depending on the resources available from the two institutions involved, a possible joint research project is defined, within a framework of mutual cooperation, in which both parties contribute their knowledge in the development and in the application of different techniques in previously agreed areas to be studied and worked on.
Institut Geològic de Catalunya (IGC); Universidad de Salta, Argentina.
Financed by: Spanish Agency for International Development Cooperation (Agencia Española de Cooperación Internacional para el Desarrollo - AECID), Spain.
COSMO SkyMed (2010)
As part of the project for the exploitation of SAR products (Synthetic Aperture Radar), of the small satellites constellation for Mediterranean basin observation (COnstellation of small Satellites for the Mediterranean basin Observation, COSMO-SkyMed), the ICC participated with the proposal "Continuous subsidence monitoring using COSMO-SkyMed constellation".
The proposed project was based on the use of the COSMO-SkyMed constellation for generating high quality terrain deformation maps, using Differential Interferometry SAR (DInSAR). Polarimetric and high resolution capabilities of the constellation are an improvement of the current results. These data, combined with ERS-1/2, ENVISAT, ALOS, TerraSAR-X and Radarsat-2 provided great series that will allow the detection of ground deformation movements, usually slow, caused by mining, overexploitation of aquifers, infrastructures building or natural processes. DInSAR results were compared with field measurements, and were validated using geological and geophysical information of the subsurface to identify and characterize the causes of subsidence as well as to evaluate their dangerousness.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI), Italy.
Financed by: Without economic consideration.
SISPYR. Seismic Information System of the Pyrenees (2009-2013)
The programme goals are the implementation of a common system for earthquakes data acquisition and a better adaptation of the scientific means for the preparation of the management of the seismic crisis in the Pyrenees massif.
Institut Geològic de Catalunya (IGC); Bureau de Recherches Géologiques et Minières (BRGM), France; Observatoire Midi-Pyrénées, France; Instituto Geográfico Nacional, Spain; Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC), Spain.
Financed by: ERDF Fund (POCTEFA programme 2007-2013); Région Languedoc Roussillon.
[+info:] SISPYR
IMERNET: Ibero-maghrebian network for the seismic hazard reduction (2008-2012)
Earthquakes do not recognize borders and the great collisions that take place in the ibero-maghrebian region, which includes Algeria, Morocco, Portugal, Spain and Tunisia, can affect some of these countries. This project is also the framework to reinforce the importance of bilateral or multilateral collaborations for research and development, training, technology transfer and the exchange of data and staff.
Algeria: Centre de Recherche en Astronomie et Géophysique, Centre National de Recherche Appliquée en Génie Parasismique, Université de Bab Ezzouar. Morocco: Institut Scientifique, Université Mohammed V, Centre National pour la Recherche Scientifique et Technique. Portugal: Instituto de Meteorologia, Universidade de Évora. Tunisia: Institut National de la Météorologie. Spain: Institut Geològic de Catalunya (IGC), Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Real Instituto y Observatorio de la Armada (ROA), Instituto Geográfico Nacional.
Financed by: Participating institutions.
CASABLANCA. Exchange of experiences on ocean bottom seismoters (OBS) among Mediterranean tsunamis observers (2008-2009)
This project means an improvement of the Catalan seismic network. The OBS pressure sensor will participate in the European network for predicting tsunamis in the western Mediterranean. The exchange of experiences between Catalonia and Nice is of great interest, taking into account that the implementation of the permanent ocean bottom seismoter (OBS), integrated into a real-time seismicity network, was pioneer in Spain.
Institut Geològic de Catalunya (IGC); Observatori de l'Ebre, Spain; Centre Geosciences Azur - Geoazur, France.
Financed by: Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación, Spain.
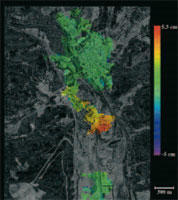
Interferometry for determination of subsidence in Bogotá-2 (2008-2009)
This DInSAR study was undertaken to determine the evolution of land subsidence in the city of Bogotá during the period 2006-2008, and to evaluate the potential of DInSAR as a tool for monitoring mass movement phenomena. The results led to the subsequent adoption of measures to prevent the risk of subsidence, in addition to the following actions; quantification of vertical land displacements and of the speed at which these displacements occur; division into zones in accordance with the levels of subsidence; assessment of the influence of winter periods on the occurrence of this phenomenon; evaluation of the potential of the tool for monitoring mass movement phenomena; and definition, based on the results, of the needs for future monitoring and for extending the knowledge acquired.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Fondo de Prevención y Atención de Emergencias de Bogotá, D.C. (FOPAE), Colombia.
Financed by: Fondo de Prevención y Atención de Emergencias de Bogotá, D.C. (FOPAE), Colombia.
SISNEPI. Use of advanced techniques for integrated studies on seismicity, surface structure and seismic hazard in the northeast of the Iberian Peninsula (2007-2010)
This project aims to specify the exposure to geo-environmental hazards, particularly seismic, in the northeast of the Iberian Peninsula, by improving the knowledge on aspects that are essential for the assessment of seismic hazards, among which the surface structure of the crust, the characterization of seismicity and the determination of soil movement as a consequence of earthquakes.
Institut Geològic de Catalunya (IGC).
Financed by: Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación, Spain.
NERIES. NEtwork of Research Infrastructures for European Seismology (2006-2010)
The project goals are the monitoring and understanding of the earthquakes processes and the mitigation of their effects. With this purpose, the NERIES project integrates research infrastructures related to the study of seismicity.
NERIES is a consortium of 25 universities and research centers that share the experience and the infrastructures in the field of seismology: ORFEUS, EMSC, ETHZ, KNMI, UU, CEA-LDG, UJF- LGIT, IPGP, GFZ, UP, INGV, DPC-SAPE, Imperial, BGS, NORSAR, ITSAK, KOERI, FFCUL, IST, IGC, AWI, UNLIV, NIEP, ZAMG, NOA-IG.
Financed by: EU 6th Framework Programme (Integrated Infrastructure Initiatives).
[+info:] NERIES
RISTE-COSTE. Effects of earthquakes and tsunamis in Spanish coastal areas (2006-2009)
Assessment of effects of soil movement caused by earthquakes that take place in the Gulf of Cádiz and the effects of tsunamis in the Bay of Cádiz and various points of the Spanish Mediterranean coast.
Institut Geològic de Catalunya (IGC); Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain; Real Instituto y Observatorio de la Armada (ROA), Spain.
Financed by: Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación, Spain.
Interferometry for determination of subsidence in Bogotá-1 (2006-2007)
The ICC undertook a study by means of differential interferometric synthetic aperture radar (DInSAR) techniques, in order to determine the evolution of land subsidence in the city of Bogotá during the period 1992-2005.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Fondo de Prevención y Atención de Emergencias de Bogotá, D.C. (FOPAE), Colombia.
Financed by: Fondo de Prevención y Atención de Emergencias de Bogotá, D.C. (FOPAE), Colombia.
Consolidated Group of Research: Active geological processes and hazard (2005-2013)
The main goal of the research group is the study of active geological processes and danger. For this purpose, a study of identification of the active processes, analysis of the phenomena, monitoring of the processes and catalogue of active geological processes is basic. First, a detailed study of each type of risk is necessary, and it will be carried out by different work teams (seismology, landslides, subsidences, snow avalanches ...) and, in parallel, a multi-hazard study will be devoted to evaluate the methodologies for processing this data in an integrated way.
Institut Geològic de Catalunya (IGC).
Financed by: DURSI (Government of Catalonia), Spain.
Methodology for the risk management of ground movement under the scene of insurances policy (RISCMASS) (2004-2006)
Project that studies the land movements, by means of radar interferometry, geophysical studies and establishment of a leveling network for the definition of the land movements models, elaboration of risk maps and analysis on the insurance policies. The role of the ICC in this project was to work on a pilot zone (potassium river basin) undertaking the analysis of the problem by means of radar interferometry, geophysical studies and establishment of a leveling network. A data base and a GIS on the risks of the movements of the land in this zone was designed and implemented.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche-Istituto di Ricerca per la Protezione Idrogeologica (CNR-IRPI), Regione Calabria, Italy; Protezione Civile, Regione Siciliana, Italy; Universitat d’Alacant, Spain; National Observatory of Athens (NOA), Greece.
Financed by: INTERREG IIIB MEDOC program.
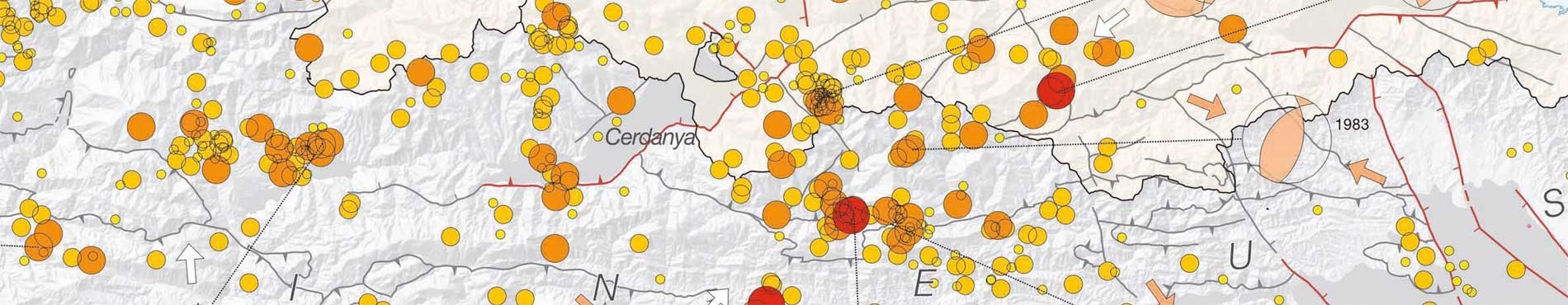
ERSE. Realistic scenarios of seismic hazard in Spain (2003-2006)
Assessment of seismic effects in Malaga and La Cerdanya. Comparison with real damages caused by the earthquakes of Girona (1428) and Malaga (1680).
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain; Real Instituto y Observatorio de la Armada (ROA), Spain.
Financed by: Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia, Spain.
CASABLANCA. Characterization of the detectability of a permanent Ocean Bottom Seismometer (OBS), for the study of seismicity and seismic hazard (2003-2006)
The project includes the development and implementation, for the first time in Spain, of a permanent Ocean Bottom Seismometer (OBS), integrated in the seismic network in real time, installed about 50 km off the coast of Tarragona, near the Casablanca oil platform. In addition to the seismic sensor, a pressure sensor has been installed to be used, among other applications, to detect marine waves caused by submarine earthquakes.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Observatori de l'Ebre, Spain; RSE, Spain; Repsol, Spain.
Financed by: Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia, Spain.
Automatic Information of seismic damages (ISARD) (2003-2006)
The aim of this project is the transborder and unified zoning of the Pyrenees to obtain preventive and operational informations of the seismic risk, without the distortion that could cause the Spanish-French border. It foresees the installation of 3 accelerographs in France, 2 seismic stations in Catalonia and 1 accelerograph in Andorra, and fine tunning of the automatic system of damages estimation.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Bureau de Recherches Géologiques et Minières (BRGM), Montpellier, France; Centre Scientifique et Technique du Bâtiment, Champs-sur-Marne, France; Direcció General d'Emergències i Seguretat Civil (Generalitat de Catalunya), Barcelona, Spain; Ajuntament de Puigcerdà, Spain; Centre de Recerques en Ciències de la Terra, Andorra.
Financed by: Fondos FEDER de la Unión Europea (programa INTERREG III).
Seismic risk in Andorra (2002)
The geotechnics data summary of different zones of the valley has been carried out in order to characterize the dynamic parameters of the valley ground. With these data the functions of seismic transference with an equivalent 1D linear method (proShake) have been estimated. On the other hand, a campaign to register of the seismic noise has been carried out to characterize, experimentally, the predominant periods of grounds answers. Taking all this into account a preliminary seismic shaping has been defined.
The possibility of slidings produced by earthquakes has also been studied. A methodology developed in California has been adapted and it has been applied to the lithologies and existing slopes in Andorra, using values similar to those of the studies of danger made in the Pyrenean zone as an input earthquake.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Institut d'Estudis Andorrans, Andorra.
Financed by: Undertaken jointly by the participating institutions.
Study of the seismic local effects in Andorra (2002)
Preliminary study of the seismic microbanding in most urbanized areas of Andorra that includes the estimation of the amplification functions of the earthquake, both in the zone of the valleys and in the mountainous slopes, and a study of the danger of generation of avalanches caused by earthquakes.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Institut d'Estudis Andorrans, Andorra.
Financed by: Undertaken jointly by the participating institutions.
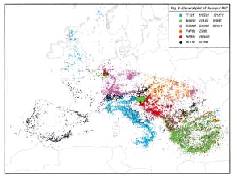
European-Mediterranean Seismic Hazard Map 1:5,000,000 (2002-2003)
Development of edition processes and publication of the map.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); European Sismological Commission and International Geological Correlation Program.
Financed by: Schweizerischer Erdbebendienst (SED), Zurich, Switzerland.
Seismic of reflection of the Principality of Andorra (2002-2003)
Geophysical study in the bucket of glacier overexcavation at Andorra la Vella (from Santa Coloma to Andorra la Vella).
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Centre de Recerca en Ciències de la Terra (CRECIT), Encamp, Andorra.
Financed by: Centre de Recerca en Ciències de la Terra (CRECIT), Encamp, Andorra.
Evaluation of seismic hazard, soil effects and soil-structure interaction in an instrumented basin (EUROSEISRISK) (2002-2004)
The aim of the project is the validation of computing codes, both of the effects of local amplification and of the soil-structure interaction of seismicity in the Volvi-Thessaloniki valley.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece; Institute of Engineering Seismology and Earthquake Engineering, Thessaloniki, Greece; Laboratoire Central des Ponts et Chaussées, Paris, France; Rheinisch-Westfälische Technische Hochschule Aachen, Germany; Università degli Studi di Trieste, Italy; University of Tokyo, Japan; Univerzita Komenského, Bratislava, Slovakia.
Financed by: Programme Energy, Environment and Sustainable Development of the European Union.
Thematic Network of Physics, Geology and Engineering of Earthquakes (2001-2006)
Organization of working meetings aimed at promoting the collaboration between the researchers of the different member groups and also of external groups invited to participate.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Enginyeria del Terreny, Cartogràfica i Geofísica (UPC), Spain; Observatori Fabra, Spain; Observatori de l'Ebre, Spain; Física de la Terra (UB), Spain; Departament de Geodinàmica i Geofísica (UB), Spain; Física de terratrèmols i els seus efectes (ICTJA-CSIC), Spain; Institut de Ciències de la Terra Jaume Almera (CSIC), Spain.
Financed by: DURSI (Government of Catalonia), Spain.
Seismic network of the Dominican Republic (2001)
In the scope of the project works where carried out for the inspection of the installation of a surveillance seismic network and an accelerometer network, as well as of their operation during the 1998-2000 period. The corresponding reports where delivered to AURENSA, the supervising organism for the tasks of seismic risk in Dominican Republic undertaken by different national and international organisms on behalf of the European Union.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); AURENSA, Madrid, Spain.
Financed by: European Union.
Advanced methodology for seismic risk scenarios with applications in European cities (RISK-UE) (2001-2003)
The aim of this project is to develop a general and modular methodology for the accomplishment of seismic damage scenarios, considering the specificities of European cities, including buildings and historical sites. It is based on the evaluation of the seismic danger, on the systematic inventory and the tipologies of the elements at risk and the analysis of the value and the vulnerability of these elements. The methodology will be applied in seven European cities, Barcelona among them.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Institute of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Seismology (IZIIS), Skopje, Macedonia; Universitatea Tehnică de Construcții din București (UTCB), Bucharest, Romania; Politecnico-Structural Engineering Department (POLIMI), Milan, Italy; Land Use Planning and Natural Risks (BRGM), Marseille, France; Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece; Laboratory of Seismic Mechanics and Earthquake Engineering, Sofia, Bulgaria.
Financed by: Directorate General XII for Science, Research and Development of the European Union.
Pianure alluvionali and Che cosa è una carta geologica? (1999-2000)
Preparation and publication in Italian of the English booklet "Alluvial Plains" (produced by: ICC, Servizio Cartografico e Geologico de la Regione Emilia-Romagna, Rijks Geologische Dienst of The Netherlands and Magyar Geológiai Szolgálat of Hungary) and of the Catalan booklet "Què és un mapa geològic?" ("What is a geological map?", published by the ICC).
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Servizio Cartografico e Geologico of the Regione Emilia-Romagna, Bologna, Italy.
Financed by: Servizio Cartografico e Geologico of the Regione Emilia-Romagna, Italy.
PALEOSIS (1998-2000)
A project of two years duration to evaluate the potentiality of large earthquakes in areas where there is currently little seismic activity. The basis of the methodology used is that repeated coseismic movements on a fault with young sediment lead to the availability of records of earthquakes in the form of typical morphological expressions.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Observatoire Royal de Belgique, Brussels, Belgium; Geologisches Landesamt, Germany; Institut de Protection et de Sûreté Nucléaire, Paris, France; Istituto di Ricerca sulla Tettonica Recente, Italy; Geologische Dienst Nederland, The Netherlands; Koninklijk Nederlands Meteorologisch Instituut (KNMI), The Netherlands; Universität zu Köln, Germany.
Financed by: Directorate General XII for Science, Research and Development of the European Union.
Research with seismic refraction in the area of Aínsa (1997-1998)
Completion of seismic profiles with a depth of 500-600 metres, in order to define the Geological evolution of the Aínsa basin (Aragon).
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Department of Geological Sciences of the University College London, United Kingdom.
Financed by: Department of Geological Sciences of the University College London, United Kingdom.
European Alluvial Plains (1996-1997)
The aim of this project was to produce a scientific publication in the form of a book about the geology of alluvial plains, their formation and the interrelation with the posible risks arising from the arrival of Man in these plains.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Servizio Cartografico e Geologico of the Regione Emilia-Romagna, Bologna, Italy; Rijks Geologische Dienst, Haarlem, The Netherlands; Magyar Geológiai Szolgálat, Budapest, Hungary.
Financed by: Undertaken jointly by the participating institutions.
EUROSEISMOD. Development and experimental validation of Advanced modelisation techniques in seismology and seismic engineering (1996-1998)
Continuation of the EUROSEISTEST project. Development of methods for the modelization of ground movement and the structures produced by earthquakes and validation of these by experiments in the Volvi-Thessaloniki network 1D, 2D and 3D, and linear and non-linear methods are considered, and an assessment is made of seismic microbanding methods in urban areas and their application to several European cities: Thessaloniki, Barcelona, Benevento, Nice, Grenoble, Lisbon and Liège.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece; Laboratoire de Géophysique Interne et Tectonophysique (Université de Grenoble), France; Institute of Engineering Seismology and Earthquake Engineering, Thessaloniki, Greece; Laboratoire de Géologie de l'Ingénieur, d'Hydrogéologie et de Prospection Géophysique, Liège, Belgium; Centro de Geofisica da Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal; Istituto di Geodesia e Geofisica, Trieste, Italy; National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Greece; Instituto Superior Tecnico, Lisbon, Portugal; Centre d'Études Techniques de l'Équipement, Aix-en-Provence, France; Laboratoire de Ponts et Chaussées, Nice, France; Laboratoire de Mécanique des Sols, Structures et Materiaux, Paris, France; Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, Barcelona, Spain; Aalborg Universiteit, Denmark.
Financed by: Directorate General XII for Science, Research and Development (Programme: Environment and Climate) of European Union.
Installation of a digital seismic network to observe the seismicity of the Salta region (Argentina) (1995-1996)
This project consisted in the development of portable personal computer-based digital equipment for the capture of seismic data, and putting this into operation in Salta (Argentina). The data recorded with this digital seismic network was subsequently analyzed.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Universidad Nacional de Salta, Argentina; Museo Nacional de Ciencias Naturales (Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas CSIC), Madrid, Spain; Instituto Andaluz de Geofísica y Prevención de Desastres Sísmicos, Granada, Spain.
Financed by: Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia (Programme of Cooperation with Latin America), Madrid, Spain.
A basic European earthquake catalogue and a database for the evaluation of long-term seismicity and seismic hazard (BEECD) (1995-1997)
The aim of this project was to begin to compile a European seismic catalogue with homogeneous criteria that is appropriate for the evaluation of seismic hazard. An important part of the project consisted in establishing rigorous methods for the elaboration of seismic catalogues, with respect to both historical and instrumental seismicity data.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche (CNR), Milan, Italy; Geo Forschung Zentrum, Potsdam, Germany; Imperial College London, United Kingdom; Osservatorio Geofísico Sperimentale, Trieste, Italy; National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Greece; Schweizerisch Erdbebendienst, Zurich, Switzerland; British Geological Survey, Edimburg, United Kingdom; Istituto Sperimentale Modelli e Strutture, Bergamo, Italy.
Financed by: Directorate General XII for Science, Research and Development (Programme: Environment) of the European Union.
ResPyr (1995-2005)
Research project to study cortical movements on both sides of the Pyrenees using space geodesy methods and techniques. The project stages for 1995 and 1997 are: first observation campaign in the eastern part of the Pyrenees (1995); first observation campaign in the western part of the Pyrenees (1997).
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Observatoire Midi-Pyrénées, Toulouse, France; Universitat de Barcelona, Spain; Escola d'Enginyers Tècnics en Topografia (Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya), Barcelona, Spain.
Financed by: Undertaken jointly by the participating institutions.
Comparative testing of strong ground motion accelerographs at Veletri, Italy (1994-1995)
The aim of this project was to carry out some comparative operational tests on different systems for recording earthquake strong ground motions, in particular comparing a system developed at the ICC with other systems commercially available in Italy.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Ente Nazionale della Energia Elettrica (ENEL), Roma, Italy; Ente per le Nuove Tecnologie, l'Energia e l'Ambiente (ENEA), Roma, Italy.
Financed by: Foreign ministries of Italy and Spain.
Radar Interferometry (1993)
Development of a prototype and workshop to present the capabilities of radar interferometry, especially in the field of the phenomenon of subsidence, problem analysis and monitoring.
Servei Geològic de Catalunya (SGC); Instituto Nacional de Estadística, Geografía e Informática (INEGI), Mexico.
Financing: Participating organizations.
Completion of seismic reflection profiles on the island of Reunion as part of a project to study volcanic risk (1993)
The aim of this project was to investigate the possibility of detecting the 3D heterogeneity of the active volcano Piton de la Fournaisse through the completion of several seismic experiments testing different source-receiver geometries.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC) and other participating institutions: Laboratoire de Sismologie Expérimentale (Institut Physique du Globe), Paris, France; Institut de Ciències de la Terra Jaume Almera (Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas CSIC), Barcelona, Spain; École et Observatoire de Physique du Globe (EOPG), Strasbourg, France; Université de Pau, France; Office pour la Recherche Scientifique et Technique d'Outremer (ORSTOM), Villefranche-sur-Saone, France.
Financed by: Directorate General XII for Science, Research and Development (Programme: Environment) of the European Union.
Study of the earthquake of the year 1373 in the central Pyrenees (1993-1994)
The aim of this project was to compile and analyse documentary archive information about the earthquake that occurred in the central Pyrenees in the year 1373, its historical analysis and seismological interpretation, and contribution to the evaluation of seismic hazard.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Bureau de Recherches Géologiques et Minières (BRGM), Orleans, France; Observatoire Royal de Belgique, Brussels, Belgium; Departament d'Història Medieval (Universitat de Barcelona), Spain.
Financed by: Departament de Política Territorial i Obres Públiques (DPTOP) of the Generalitat de Catalunya, Barcelona, Spain; Bureau de Recherches Géologiques et Minières (BRGM), France; Observatoire Royal de Belgique, Belgium; Universitat de Barcelona, Spain.
EUROSEISTEST. Volvi-Thessaloniki: A European test site for Engineering Seismology and Seismology (1993-1996)
The aim of this project was to study the influence of sediment on earthquake ground motion and its effects on structures. A test site was established at Volvi-Thessaloniki, where a series of sensors were installed with their corresponding data adquisition systems, in order to obtain detailed information about the ground motion in areas with differing geotechnical characteristics. Several campaigns applying geophysical and geotechnical methods were completed, in order to determine the characteristics of the subsoil, and a scale model building was build and monitored.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece; Laboratoire de Géophysique Interne et Tectonophysique (Université de Grenoble), France; Institute of Engineering Seismology and Earthquake Engineering, Thessaloniki, Greece; Université de Liège, Belgium; Istituto di Geodesia e Geofisica, Trieste, Italy; National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Greece; Laboratorio Nacional de Engenharia Civil (Instituto Superior Tecnico), Lisbon, Portugal; Centre d'Études Techniques de l'Équipement, Aix-en-Provence, France.
Financed by: Directorate General XII for Science, Research and Development (Programme: Environment) of the European Union.
Seismic instrumentation techniques applied to volcanology. Experimentation in Antarctica (1992-1993)
The aim of this project was to develop seismic instrumentation and to apply it to the recording of seismic activity associated with volcanism in Deception Island.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC) and other participating institutions: Museo Nacional de Ciencias Naturales (Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas CSIC), Madrid, Spain; Instituto Andaluz de Geofísica y Prevención de Desastres Sísmicos, Granada, Spain.
Financed by: Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia (Programme: Antártico), Madrid, Spain.
Implementation of methods for the calculation of earthquakes strong motion. Application to the Ashigara Valley experiment (Japan) (1992-1994)
The aim was to adapt and develop programs for the analysis of local effects on the earthquake ground motion. Application to soil response in the Ashigara Valley international experiment in Japan.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Laboratoire de Géophysique Interne et Tectonophysique (Université de Grenoble), France.
Financed by: Departament de Política Territorial i Obres Públiques (DPTOP) of the Generalitat de Catalunya, Barcelona, Spain; Laboratoire de Géophysique Interne et Tectonophysique (Université de Grenoble), France; Centre Interdepartamental de Recerca i Innovació Tecnològica (CIRIT), Barcelona, Spain.
Seismicity study methods - instrumental networks (1991-1995)
Installation and adaptation of machines and programs for telephonic transmission and analysis of seismic data in Catalonia.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Laboratoire de Géophysique Interne et Tectonophysique (Université de Grenoble), France.
Financed by: Undertaken jointly by the participating institutions.
PotSis: Seismic Potentiality (1991-2001)
Project of investigation to quantify the current distribution of tectonic deformations, in order to be able to estimate the return periods of destructive seisms in the eastern Pyrenees, applying geodesic techniques to measure recent cortical movements. This interdisciplinary project includes geodesic and seismological studies, studies of neotectonics and historical seismicity, etc. Project stages worthy of mention are: design and establishment of the network (24 vertices); a first campaign of observations (1992); calculation of the data of the first PotSis'92 campaign; a second campaign of observations (1994); calculation of the data of the second PotSis'94 campaign; analysis and comparison of both periods. Due to the nature of the area and the work, significant results are expected during a timespan of at least 10 years.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Institut de Protection et de Sûreté Nucléaire, Paris, France; Observatoire Midi-Pyrénées, Toulouse, France; Université Montpellier II, France; GEOID, Montpellier, France; Géologie Tectonique, Environnement et Risques, Montpellier, France; Université des Sciences et Technique du Languedoc, Montpellier, France; technique contribution of the Institut für die Anwendung der Geodäsie in dem Bauwessen, Stuttgart, Germany.
Financed by: Departament de Política Territorial i Obres Públiques (DPTOP) of the Generalitat de Catalunya, Barcelona, Spain; Institut de Protection et de Sûreté Nucléaire, France; Observatoire Midi-Pyrénées, France; GEOID; Géologie Tectonique, Environnement et Risques, France; Université des Sciences et Technique du Languedoc, France.
Determination of earthquakes parameters from records obtained in the SMART-1 strong motion accelerometer array in Taiwan (1990-1992)
The aim of this project was to develop and apply methods of analysis of strong ground motion accelograms, in order to obtain focal parameters of earthquakes.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC) and other participating institutions: University of California, Berkeley, USA.
Financed by: Departament de Política Territorial i Obres Públiques (DPTOP) of the Generalitat de Catalunya, Barcelona, Spain.
Observation and analysis of seismicity in the Pyrenees (1990-1995)
The aim of this project was to establish, operate and process data from a seismic network observing the central-eastern Pyrenees. Data from the field stations was sent via Meteosat satellite to the reception centres in Barcelona and Toulouse. The result of the analysis of this data is published in the joint annual bulletins "Seismic activity in the Pyrenees".
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Observatoire Midi-Pyrénées, Toulouse, France.
Financed by: Undertaken jontly by the participating institutions.
Research of Historical Seismicity in Europe (RHISE) (1989-1993)
The aim of this project was to review some historical European earthquakes that principally occurred in border areas. As a result, the community was provided with a set of data that is very useful in the analysis of seismic hazard, while common methodologies were established between European seismologists and historians working in this field.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC) and other participating institutions: Istituto per la Geofisica della Litosfera del Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche (CNR), Milan, Italy; Bureau de Recherches Géologiques et Minières (BRGM), Marseille, France; Imperial College London, United Kingdom; Observatoire Royal de Belgique, Brussels, Belgium; National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Greece; Centre Sismologique Euro-Mediterranéen, Strasbourg, France; Instituto Nacional de Meteorologia e Geofisica, Lisboa, Portugal.
Financed by: Directorate General XII for Science, Research and Development of the European Union.
Iberian Lithosphere Heterogeneity and Anisotropy (ILIHA) (1988-1990)
The aim of this project was to investigate the lateral and vertical heterogeneity and the seismic anisotropy of the lithosphere in the Hercynian domain of the Iberian peninsula through the execution of deep seismic profiles on a large scale and the application of other techniques to analyse data from broadband seismic stations.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC) and other participating institutions: Instituto Geográfico Nacional (IGN), Madrid, Spain; Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain; Universitat de Barcelona, Spain; Real Instituto y Observatorio de la Armada (ROA), Cádiz, Spain; Instituto Nacional de Meteorologia e Geofisica, Lisboa, Portugal; Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal; Universität Friedericiana Karlsruhe, Germany; Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris, France; Université Louis Pasteur, Strasbourg, France; Rijksuniversiteit Utrecht, The Netherlands; University of Leicester, United Kingdom; Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies, Dublin, Ireland; Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche (CNR), Roma, Italy; Københavns Universiteit, Copenhagen, Denmark.
Financed by: Directorate General XII for Science, Research and Development of the European Union.

 Contact
Contact