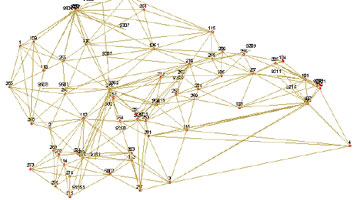
EPN Densification Analysis Center (2015)
The ICGC was accepted by EUREF as a Dedicated Analysis Center (DAC), with the goal of calculating daily the precise coordinates of a network of 156 GNSS stations, with the final objective of supporting the calculation of a dense and accurate velocity field for Europe. The network includes the Pyrenees, the Betic System, the eastern Mediterranean coast of the Iberian Peninsula and the Balearic Islands.
Calculation of precise coordinates of a GNSS reference station (2013)
The Government of Andorra acquired a GNSS reference station and moved it to its headquarters to manage it. The ICC calculated the precise coordinates of this GNSS reference station.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Ministeri d’Economia i Territori (Govern d’Andorra).
Financed by: Ministeri d’Economia i Territori (Govern d’Andorra).
Validation of reference network in Morocco (2007-2008)
The ICC undertook the calculation and validation of the Moroccan reference network, formed by 24 points that were used to determine the basic network within the ITRF 05 system. It also completed the transformation of coordinates between the Gharb system and the new RFM reference system. This task consisted in: observation of a number of basic lines between the RFM system and the Gharb system, recalculation of old points in the new reference system in order to deduce the transformation networks between the two systems, and determination of the coordinates of the 29 points in the RFM system within the Gharb coordinates system.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Agence Nationale de la Conservation Foncière, du Cadastre et de la Cartographie (ANCFCC), Morocco.
Financed by: Agence Nationale de la Conservation Foncière, du Cadastre et de la Cartographie, Morocco.
WART-EGAL project (2005-2006)
The principal aim of the project was to gauge the potential of the EGNOS RIMS network (European network of permanent stations for EGNOS) to provide support for subdecimetric navigation in real time based on the WART technique. This gave impetus to the aforementioned service throughout Europe, and the metric accuracy of the EGNOS system will be improved by the subdecimetric accuracy of the WART system.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya; Geodeettinen Laitos, Finland; Pildo, Spain; IFEN, Germany.
Financed by: Galileo Joint Undertaking (European Union and ESA).
PARAMOUNT. Public Safety & Commercial Info-Mobility Applications & Services in the Mountains (2002-2003)
The aim of the project is to develop a location service for hikers and rescue services in the Alps and the Pyrenees, where two test areas have been defined. There are plans to develop three types of services: Infotour, will provide the user with a variety of local information and navigation directions; Safetour, will provide information related with mountain safety, and Datatour will involve users in the acquisition and maintenance of the PARAMOUNT database. Communication between the servers that will provide the aforementioned information and the mobile devices will be achieved by means of GPRS technology. The data will be transferred via HTTP protocol using XML.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); IfEN Gesellschaft fuer Satellitennavigation mbH, Poing, Germany; AGIS, Universität der Bundeswehr, Poing, Germany; Bayerische Bergwacht, Germany; Österreichischer Bergrettungsdienst, Austria.
Financed by: Programme IST of the European Union.
GPS reobservation of the geodetic network and preliminary study of the geoid of the Principality of Andorra (1999)
The aim of this project was to obtain an accurate geodetic network, to determine the accuracy of the various geoids available, and to estimate the cost of the gravimetric campaign needed, in order for a local geoid to be calculated with the required accuracy to enable topographic and cartographic work to be undertaken. Therefore, the 59 vertices that form the principal and secondary geodetic network of the Principality of Andorra were reobserved by means of GPS technology and adjusted; 20 points were monumentalized, measured by means of GPS technology and leveled, in order to determine the accuracy of the geoids available; and simulations were made to determine the configuration and the density of the gravimetric campaign data needed, in order to calculate a local geoid with the required accuracy.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Ministeri d'Ordenament Territorial (Govern d'Andorra).
Financed by: Ministeri d'Ordenament Territorial (Govern d'Andorra).
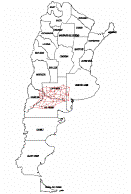
Technical assistance project for the Argentinian mining sector (PASMA) (2nd part) (1999-2000)
The aim of this project is to carry out the work with relation to the geodetic mining subnetwork (GPS) and to reposition boundaries of mines for which licenses have been granted in the south-north region, which includes the provinces of La Pampa, Río Negro, Neuquén and Buenos Aires.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Subsecretaría de Minería de la Nación of the Secretaría de Industria, Comercio y Minería, Buenos Aires, Argentina.
Financed by: Banco Internacional de Reconstrucción y Fomento (BIRF). World Bank.
MAGIC. Meterological Applications of Global Positioning System Integrated Clumn Water Vapor Measurements in the Western Mediterranean (1998-2001)
The project aims to determine the water vapor content in the atmosphere by modeling the time lag of the observations of the permanent GPS stations.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Mécanique Appliquée et Sciences de l'Environnement (ACRI), France; Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS), Montpellier, France; Institut d'Estudis Espacials de Catalunya (IEEC), Barcelona, Spain; Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI), Italy; Università degli Studi di Modena (UMOD), Italy; Danmarks Meteorologiske Institut (DMI), Denmark; Real Instituto y Observatorio de la Armada (ROA), Cádiz, Spain.
Financed by: Directorate General XII for Science, Research and Development of the European Union.
Technical assistance project for the Argentinian mining sector (PASMA) (1997-1998)
The objective was the supervision of the topogeodetic work of the GPS geodetic mining subnetwork by obtaining GPS control points for the georeferencing of satellite images and the repositioning of the mining concession boundaries in the provinces of Salta, Catamarca, La Rioja, San Juan, Mendoza and San Luis. The topogeodetic work planned consisted of installing various fiducial stations which are integrated into the world-wide IGS network, the use of the IGS network data in order to adjust the entire geodetic network of the Argentinian subcontinent and the calculation of the geoid, necessary to obtain an altimetric accuracy (Z) similar to that obtained in planimetry (X and Y).
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Subsecretaría de Minería de la Nación of the Secretaría de Industria, Comercio y Minería, Buenos Aires, Argentina.
Financed by: Banco Internacional de Reconstrucción y Fomento (BIRF). World Bank.
Gravimetric flight in the Rocky Mountains in Canada (1996)
Participation in a test gravimetric flight over the Rocky Mountains in Canada with the ICC's Litton LTN-101 inertial system, together with other inertial systems.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Department of Geomatics Engineering of the University of Calgary, Canada.
Financed by: Undertaken jointly by the participating institutions.
Tropospheric delay of GPS signals (1996-1997)
Integrated initiative which aimed to exchange knowledge and experience in the creation of models to represent the tropospheric delay affecting GPS signals.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); University of Nottingham, United Kingdom.
Financed by: Dirección General de Investigación Científica y Técnica, Madrid, Spain.
RASANT (1995-1997)
Project for the development and implementation in Catalonia of the RASANT differential correction broadcasting system for real time positioning. The stages of the project were: study of the system and its application to Catalonia; introduction into Region I in an experimental phase; definitive introduction into Region I and progressively throughout Catalonia. The broadcast of differential corrections from Collserola with coverage over Barcelona, with an accuracy of 3 to 5 metres was archieved in 1996.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Landesvermessungsamt Nordrhein-Westfalen, Germany.
Financed by: Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC).
Methodology for the execution of plot measurements, distances and surfaces in relation with the requirements of the integration system (1993)
Evaluation of the different methods in existence for wide-scale measurement of the perimeter and area of agricultural plots. The evaluation included the initial investment necessary, the execution time and the total cost. In short, the project was planned to help the authorities concerned in the various European countries to complete the control phase which was part of the Community Agricultural Policy. Study was made of the approximate methods (tape measure), photogrammetric methods (orthophotograph, photogrammetric stations) and topographical approaches (theodolites, GPS "Global Positioning System" stations).
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Joint Research Centre (JRC) of the European Union, Ispra, Italy.
Financed by: Joint Research Centre (JRC) of the European Union.
EPOCH'92 (1992)
Participation of the Ebre fiducial station in the IGS-Epoch'92 campaign. The fiducial stations of the ICC were incorporated into the network of permanent stations of the IGS.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); International GPS Service for Geodynamics (IGS) of the International Association of Geodesy (IAG).
Financed by: Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC).
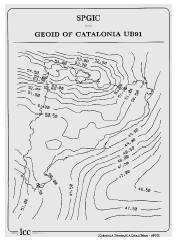
GeoCat: Geoid of Catalonia (1991-1994)
Research project to evaluate the determination of the UB'91 geoid of Catalonia by contrasting the deflections from the vertical observed during the DEFLEX'91 and DEFLEX'92 campaigns, undertaken within the framework of an agreement with the Departament de Matemàtica Aplicada i Anàlisi of the Universitat de Barcelona. The project was completed in the following stages: a first campaign of observations with a zenithal camera to determine astronomical positions (1991); evaluation of the observations of the campaign; a second campaign of observations (1994). A geoid of Catalonia was obtained with a grid density of 3' and an estimated accuracy of 1 ppm.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Institut für Geodäsie und Photogrammetrie (Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule), Zurich, Switzerland.
Financed by: Undertaken jointly by the participating institutions.
Three-dimensional cartography of the Costa Smeralda 1: 1,000 (1985)
This project provided the ICC with the necessary experience to establish the 4th order geodesic network of Catalonia. The aim of the project was the production of three-dimensional topographic information with which the urban planners of the Costa Smeralda designed their projects and could know the impact the new buildings would have on the landscape. Appropriate graphic programs were designed to eliminate much of the manual intervention in the editing processes. The project facilitated the design and calculation of the base geodetic network for the cartographic project.
Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC); Servizi Immobiliari Costa Smeralda, Sardinia, Italy.
Financed by: Servizi Immobiliari Costa Smeralda, Sardinia, Italy.

 Contact
Contact